When you walk in the room, who shows up for Read more →

Images of Goals and Metrics
From my blog posts on goal setting for leaders.
.
.
.
.
Management by Objectives? Or Leading with Goals?
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Spoiling Good Goals with Bad Metrics
.
Good Goals Gone Bad
Goals are powerful leadership tools that focus attention and effort. Good goals go bad when their power blinds us to critical information or strategic changes.
Good Goals
As a leader, goal setting is an essential part of your leadership toolbox. Like any tool, you have to use goals right:
Set SMART goals. Smart goals are specific, measurable, actionable, realistic and time-bound. Part of being realistic is making sure none of your employees have too many goals.
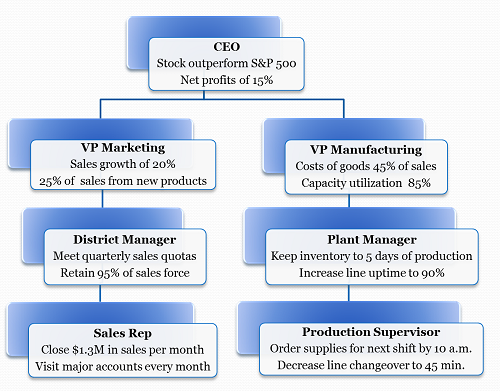
Coordinate goals. Use management by objectives to ensure goals are coordinated between people and organizations.
Provide metrics. Create goal-specific metrics to further shape and refine behavior.
If your goals are SMART, coordinated and backed by metrics, you will have a powerful leadership tool.
With great power comes great responsibility, for Spiderman and for leaders. The very power of goal setting can create problems. In my post on Got a Goal? Get A Metric! I used a photo of my power saws to illustrate the idea of goals as powerful tools.
My gloved hand is reaching for my zip saw in this picture. I love my zip saw – it is fun, powerful and fast. I also loved those gloves. Loved, because I no longer have those gloves. A day or so after David Slade took this picture, I got careless and touched the moving blade with my gloved hand. I was not injured, but the finger tip of one of my gloves was destroyed. Goals are like my zip saw – powerful, effective and potentially dangerous.
Goals Gone Bad
Here are two example of goals gone bad:
Counting Basketball Passes. Watch this video carefully and attempt to follow the directions. Done? Spoiler alert: If you haven’t watched the video yet, please do so. Most people are so focused on the goal of counting basketball passes that the gorilla goes unnoticed.
In an organization, people can get so busy meeting their goals that they miss the gorilla. A sales person gets focused on meeting their quota, and customer service goes south. A plant manager focuses intently on production and cost goals, and maintenance slips. A general manager focuses on the profit goal and doesn’t notice that employees are burning out. The gorilla – poor customer service, delayed maintenance or employee burnout – can destroy the organization, but leaders do not even notice the gorilla in the room because of their laser-like focus on meeting their goals.
Climbing Mount Everest. On May 11, 1996, a number of people were attempting to fulfill their goal of climbing Mount Everest. Climbers were intensely focused on reaching the summit. When the climbers faced delays on the ascent, they ignored declining oxygen supplies and a gathering storm to push through to meet their goal. Eight people died that day on Mount Everest. Jon Krakauer blamed a number of factors for the deaths, but one powerful factor was destructive goal pursuit. Individual climbers had planned and trained for years. Deciding to turn back would have meant giving up that cherished goal. The expedition companies competed with one another for clients. They also had an intense commitment to the goal of having clients summit Everest.
Relentless pursuit of business goals can lead to death. Auto companies pursuing low costs produce unsafe cars such as the Corvair, Pinto and Explorer. Construction companies taking short cuts on safety practices to meet project deadlines. Truckers fall asleep at the wheel attempting to make just-in-time delivery goals.
In most organizations, no one dies from relentless pursuit of goals. Instead, goal focus creates short term success and long term loss. The goals are met, but the organization alienates customers, employees or vendors.
Avoiding Goal Blindness
In both the basketball video and the fatal Everest climb, the power of the goal blinded participants to vital information. If goals are powerful, their power must be moderated. In other words, leaders are responsible for using goals wisely. Here are a couple of thoughts on how to limit the destructive power of goals:
Lead with principled moderation. As a leader, you need to be a rock in the storm. You have to take a principled stand. In my post on the leadership paradox of principled moderation, I suggest integrity and appropriate transparency as two non-negotiable leadership principles.
Take a look around. An antidote to the focusing power of goals is to shift your focus. Take your eyes off the goal at hand and look to the horizon. Encourage your people to do the same. Pause. Take a breath. Ask powerful questions: “Are we doing the right thing? How does this impact our customers? Employees? Community? Five years from now, will this still seem like a good idea?”
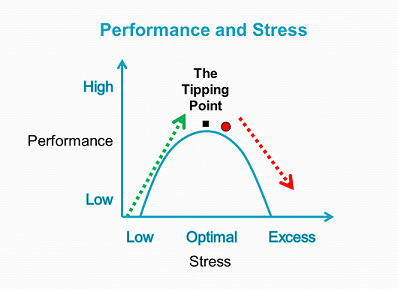
Resource properly. When people are tight on time, energy, supplies or people, they have to push harder to accomplish their goals. Pushing harder makes goal blindness more likely. The basketball video tricks most first time viewers because you have to really focus to get the count right. The Everest climbers had limited endurance and bottled oxygen to make the climb in a narrow window of time. A little more time, a few more supplies or an extra person can help you and your team avoid the tipping point of performance and avoid goal blindness.
Bottom line: Goals are powerful. Use them wisely and take precautions to avoid goal blindness. Then, you can keep your good goals from going bad.
Too Many Goals?
Goals are powerful leadership tools. They focus attention and effort on the key accomplishments needed for organizational success. If goals are good, are more goals better? As a leader, how many goals should you set?
Basics of Goal Setting
As a leader, goal setting is an essential part of your leadership toolbox. Like any tool, you have to use goals right:
Set SMART goals. Smart goals are specific, measurable, actionable, realistic and time-bound.
Coordinate goals. Use management by objectives to ensure goals are coordinated between people and organizations.
Provide metrics. Give goal-specific feedback to further shape and refine behavior. I will discuss metrics more in my next post.
No Goals are No Good
Leadership is managing energy in yourself first and then in others. Goals help you manage energy. Goals provide a destination for efforts. They give direction and quantity for work related behaviors. If you have no goals, your own efforts will be unfocused. And if you do not set goals with your team, their efforts may be unfocused also, or their efforts may be focused on things that do not contribute to the organization’s success.
Too Many Goals
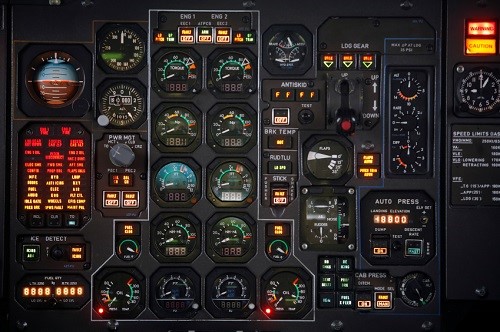
Goal setting is good, but be careful. Too many goals can backfire. The key benefit of a goal is to focus energy. More goals create more focal points. Like a busy instrument panel, too many goals can confuse and distract rather than focus attention.
So, how many goals is too many?
More than three goals is the same as no goals. When a client asks how many goals to set, I use this simple rule of thumb as a starting point.
A simple rule of thumb is better than nothing, but principles of leadership are outdated. Here are more refined ways to think about the maximum number of goals.
More goals with experience. An experienced pilot shouldn’t have trouble making sense of a plane’s control panel. An employee with years of good performance can handle more than three goals.
More goals with phased timing. If you have a complex project, a project plan might have dozens or hundreds of task goals. So long as your employee understands the project plan, the number of goals will not be an issue.
More situational goals. Some goals are relevant only in certain situations. For a retail business, you might have a SMART goal about customer wait times. If customers are not waiting, that goal is not triggered. You can have other goals about stocking or cleaning that are triggered in other situations.
In other words, the maximum number of effective goals depends on the situation your employee faces. To really know how many goals, you should have an ongoing dialogue about goals with your employees.
Goal setting. At the beginning of the performance cycle, set goals participatively. Get your employee’s sense of what is realistic.
Goal performance. While the goals are in place, keep the conversation going. Get to know their work pace and their motivations. Adjust goals as needed, whether it is the type of goal, the level or the number of goals.
Goal review. At the end of the performance cycle, evaluate performance against goals. And also evaluate the goals themselves. Ask how the goals helped or hindered performance. And be open to correcting your missteps in setting goals or supporting your employee’s performance.
Throughout the goal cycle, keep the conversation going. And, make it a dialogue. Actively listen as much as you speak.
Bottom line: Know how many goals is too many. Understand the situation each employee faces and work with them to set a realistic number of goals. And, if you have created too many goals for an employee, back off. Prioritize and consolidate goals to get the right number of goals. You will help your employees focus their attention and increase their performance.
Images of Active Listening
From my series of blog posts on active listening for leaders.
.
.
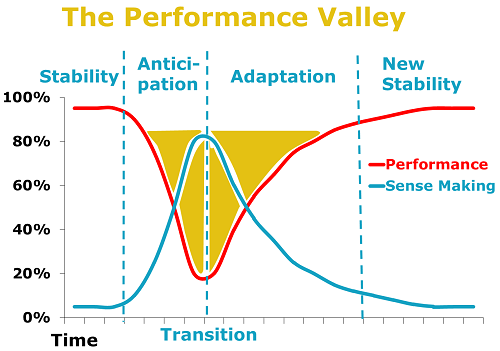 Listening in the Performance Valley
Listening in the Performance Valley
.
Energy for Active Listening
Leaders who listen well are more effective, more persuasive and more engaging than leaders who don’t listen. Carol Wilson¹ lays out five levels of listening:
1. Interrupting
2. Sharing
3. Advising
4. Attentive Listening
5. Active Listening
We have thought about Levels 1-4 in previous posts.
- You’re not listening if you’re interrupting, sharing or advising (Levels 1, 2 or 3).
- Attentive listening (Level 4) can be effective, especially in the midst of change.
Today, let’s complete the set by looking at active listening (Level 5) in more detail.
5. Active Listening
“I had the worst meeting with my boss today.”
“What happened?”
“She tore apart my financial report. I was embarrassed in front of everyone.”
“That must have been difficult.”
“You don’t know the half of it.”
“Has this happened before?”
. . .
“Why do you think she reacts that way?”
. . .
“Have you thought about what you can do?”
Active listening takes your leadership to the next level. Like attentive listening, you are focused on the other person and what they say. But you are adding more breadth and depth to the conversation. I define active listening as “the art of listening with intensity to truly hear what the other person says, knows and feels.”
The conversation about the meeting disaster gets to the heart of the issue. The other person’s feelings are validated with the reflective statement “That must have been difficult.” Causality is explored with the “Why?” question. And the other person’s problem solving is activated by asking “What can you do?”
Just the Facts?
Both attentive listening and active listening are powerful and effective tools for a leader. Both focus on the other person and help them make sense of their situation.
So what’s the difference? For me, attentive listening focuses primarily on the facts of the situation. An attentive listener asks “Who? What? Where? When?” Active listening goes beyond the facts to get to reactions and feelings. Active listening consciously explores causal factors and engages the problem solving capabilities of the other person. An active listener asks “Why? How? What’s next?”
Attentive listening focuses on the words of the other person. The active listener goes beyond just the words to notice tone, facial expression and body language. Carol Wilson describes active listening as “listening behind the words and between the words; listening to the silences; using your intuition; promoting the coachee to explore; facilitating the coachee’s self learning and awareness; making suggestions.”
If attentive listening can help shrink a performance valley, active listening is even better. When you actively listen, you have a greater opportunity to address feelings, explore causes and get the other person to solve their own problems. Then, you maximize their sense-making in the midst of change and help them get back to peak performance sooner.
Managing Your Energy
Active listening is powerful and effective. That power comes from your intensity and focus. But expending that level of power can drain your battery.
Bottom line: Active listening is hard. In a classroom exercise, I ask my students to actively listen for seven minutes. Maybe one student in thirty can actively listen for seven minutes.
Don’t be discouraged if you have trouble staying in active listening mode. Like most leadership skills, you can improve your capacity for active listening with practice. If you’re new to active listening, start small. Try this mini-experiment:
- Find someone who needs to talk. Then listen as intensely as possible for ten minutes. Notice how much time you spend in interrupting, sharing, advising, attentive listening and active listening.
- Repeat with another 10 minute listening session. Try to increase your time in active listening. It’s ok to dip into attentive listening, but minimize your interrupting, sharing and advising. Again, notice how much time you spend in each listening level.
- Keep looking for listening opportunities, gradually increasing your proportion of active listening. Then, plan to listen for 15 minutes.
With enough practice, you can achieve 50-70% active listening for an hour.
If you’re already competent at active listening, I encourage you to listen more and better. Increase your active listening capacity like a miler training for a marathon. My mini-experiment in active listening has been going for years. After every coaching session, I still do a self-evaluation of my listening. I am getting better, but I still have a way to go.
Novice or expert, practice will build your listening capacity. And, if you listen carefully, you may notice a few performance valleys shrinking.
______________________
¹Carol Wilson, “Tools of the Trade” Training Journal, July, 2010, pp. 65-66.
You’re Not Listening
Active listening is a key skill for leaders. In a previous post on Two Steps to Active Listening, I defined active listening as “the art of listening with intensity to truly hear what the other person says, knows and feels.” Leaders who actively listen are more effective, more persuasive and more engaging than leaders who don’t actively listen. It is good to know what active listening is. It is also good to know what active listening is not. Let’s look at other ways to listen.
Carol Wilson¹ lays out five levels of listening:
2. Sharing
3. Advising
4. Attentive Listening
5. Active Listening
The first three levels don’t contain the word “listening” for good reason: When you’re interrupting, sharing or advising, you’re not listening.
Levels 4 and 5 are truly listening, and we will talk about them in a later post. Today, let’s look at levels 1, 2 and 3.
1. Interrupting
“That really didn’t go well. I am worried about . . .”
“Did you see the game last night? The officiating was awful.”
When you interrupt, you build yourself up at the other person’s expense. In effect, you are saying “Be quiet because what I have to say is more important.”
How often do you interrupt others? Maybe you are rushed, anxious or annoyed. Maybe the other person has raised a topic you want to avoid. Whatever the reason, you drain energy by stepping on their airtime. A little patience, a bit of deference and a dose of etiquette will make you a better listener and a better leader.
2. Sharing
“My boss always takes credit for my work. It’s just not fair.”
“Yeah, he did the same thing to me. I made this killer presentation, but he just put his name on it and presented to the vice-president.”
With sharing, when someone shares their experience, then you share a similar experience. You may think you are reinforcing their experience, but you are really minimizing their unique situation. When the other person is speaking, you are focused on preparing your response. In other words, you are silent but not listening too hard.
When you appear to be listening, are you just waiting your turn? Do you value your experiences more than the experiences of the other person? Serve the other person by focusing on their story – your story can wait.
3. Advising
“I get really nervous when I present to the Design Group. Sometimes I shake like a leaf.”
“Try practicing in front of a mirror.”
As an accomplished professional, you have experience, expertise and insight. When someone presents you with a problem, it is easy to shift into problem solving mode.
As a problem solver, listening is critical to help you diagnose the situation so you can provide the best solution. However, it is tempting to listen only enough to figure out the problem. If your default listening mode is advising, then listening can come across as a necessary evil rather than a worthy pursuit.
Problem solving is a good thing. The problem with problem solving is we use it too much and we use it too soon. We present solutions when the other person needs dialogue. We jump to solutions instead of deep-diving issues, understanding values and exploring causality.
If someone presents you with a problem, do you quickly offer a solution? Do you listen just enough to be confident in your solution? Listen more – it will lead to better solutions. Listen longer – the other person may solve their own problem. Listen better – it will show you care.
You’re Not Listening
Interrupting, sharing and advising have two common roots. The first root may be your self-confidence. You value your own experiences, insights and problem solving capability. However, your self-confidence may bulldoze the other person’s need to be heard.
The second root may be your lack of confidence in the other person. Their conversation may show immaturity. Their wisdom seems lacking. They, after all, have come to you. If you lack confidence in them, it logically follows that you will talk more so they will talk less.
Whether you suffer from too much self-confidence or too little confidence in the other person, the end result will be too little listening on your part and too much interrupting, sharing or problem solving.
Listening Starts With Humility
The best listeners are humble. They value the other person highly. They have patience because they know the other person has important things to say. The best listeners serve by having more questions than answers. And, they would rather help the other person solve their own problems.
Notice how you listen. Notice when you shift to interrupting, sharing or problem solving. If your interruption, your story or your solution does not serve the other person, then I will give you Bob Newhart’s classic advice: stop it.
Instead, take the two steps to active listening: be quiet and value the other person. You may find the resulting dialogue leads to better insight, better solutions and a better relationship.
______________________
¹Carol Wilson, “Tools of the Trade” Training Journal, July, 2010, pp. 65-66.
Two Steps to Active Listening
Listening skills are critical for leaders. Listening opens the channels for two way communication. And it is not enough to simply be present when others are talking. You must engage in active listening, the art of listening with intensity to truly hear what the other person says, knows and feels.
I have coached b-school students, change management clients and leadership coaching clients on how to listen better. Based on those experiences, here are two steps for active listening.
1. Be Quiet
The first step to active listening is simple. Stop talking. Let the other person speak without interruption or comment from you. Surprisingly, this step is often the hardest, especially for people who are smart, driven and successful.
Sometimes we act as if silence implies consent. When someone says something wrong or they focus on unimportant aspects of the issue, we want to jump in to set things right. But you can hear without necessarily agreeing. Like a reporter interviewing politicians or a researcher gathering consumer opinions, you might not agree with what is being said, but you can stifle your impulse to speak in order to truly understand the other person’s point of view.
There is another reason to be quiet. Silence is power. In most social situations, we expect talking to fill every moment. Your silence implies personal control. Being silent means you are confident and comfortable. If you can be quiet, the other person may feel compelled to fill the uncomfortable silence.
2. Focus on the Other Party
The point of active listening is to get the other person’s perspective. To do that, you must focus on them – completely.
Use reflective listening. Repeat and paraphrase what you hear. Use phrases like “I hear you saying…” or “It sounds like…” Ask questions of clarification like “Why do you think that happened?” “When did she first say something?” or “How did that work out?” Summarize their key points. When they have given you lots of facts and reasons, try to draw out the themes. And be tentative, always checking with them to see if you understand what they are trying to say.
But it is not enough to listen to the other person’s words. You must also watch their non-verbal communication. Watch facial expressions, tone of voice and body language. Check your observations by using the phrase “You seem to feel . . .” It is especially important to notice when their words and their non-verbal communication seem to be at odds. For example, if the other person tells you they fully support a certain decision (while their eyes are downcast, their voice has no energy and their posture is slumped), follow up to see if there are some unspoken concerns.
A Difficult Conversation
Suppose you need to have a difficult conversation with someone. You may need to discuss a broken commitment, call out unacceptable behavior or give feedback on poor performance. While you might think talking more increases your chance of persuading them, you might be surprised by the power of active listening. The best difficult conversations follow this pattern:
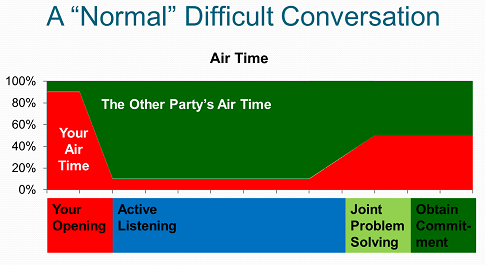 Active listening is central to this difficult conversation. By being quiet and focusing on the other party, you are helping move them toward joint problem solving and commitment. Your active listening helps them process the difficult topic. You are gaining credibility by listening. And, you will actually learn their perspective, which may change your mind about the situation and the other person.
Active listening is central to this difficult conversation. By being quiet and focusing on the other party, you are helping move them toward joint problem solving and commitment. Your active listening helps them process the difficult topic. You are gaining credibility by listening. And, you will actually learn their perspective, which may change your mind about the situation and the other person.
Difficult conversations require wisdom. Active listening is a great way to be wise. “Whoever restrains his words has knowledge, and he who has a cool spirit is a man of understanding.”¹
If you are like me, you sometimes struggle with difficult conversations. Active listening is a great way to fake wisdom. “Even a fool who keeps silent is considered wise; when he closes his lips, he is deemed intelligent.”²
A Gift
Many people live in a cone of silence. They go through most days without being heard, without being really listened to. As a leader, you can give a few minutes of your time by actively listening to the people you lead. The benefits to them and to your organization will be worth your time.
__________________________
¹Proverbs 17:27
²Proverbs 17:28
Images of the Leader’s Toolbox
Allen Slade
When I joined Ford in 1990, I sketched out an approach to leadership development called the manager’s toolbox. Words did not capture my vision, so I created a rough line drawing of a toolbox. Over the next two decades, I changed the name to the leader’s toolbox and used it with MBA classes, consulting contracts and coaching clients. In my recent posts, I used images to bring the leader’s toolbox alive.
Today’s post pulls all those images together. I invite you to examine your leadership by looking into the leader’s toolbox.
Leading on Cruise Control
The best leaders are versatile. They adjust their leadership to the needs of the moment. They are inconsistent in order to gain consistently great results.
The Leaders Toolbox
What’s in your leader’s toolbox? Don’t try to lead with duct tape and a pair of vice grips.
 Get the tools to do the job right:
Get the tools to do the job right:
Task and Person Leadership
Communication
Decision Making
Fast, Decisive Action and Slow, Deliberate Contemplation
Verbal, Quantitative and Emotional Intelligence
Using the Tools of Leadership
 Know the right leadership tool for your situation.
Know the right leadership tool for your situation.
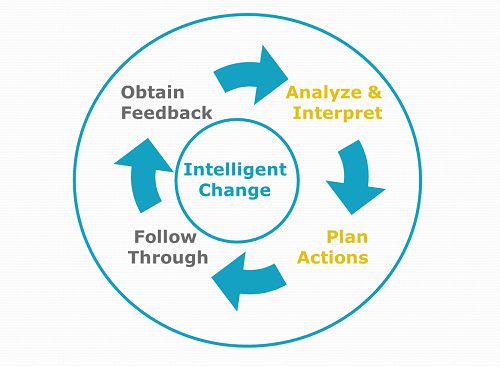
Combine appropriate risk-taking, feedback and reflection with the wisdom of a leadership coach.
Leadership Tools: Confidence
Treat confidence like a tool rather than a trait. Match your confidence to the situation to maxmize your credibility and influence.
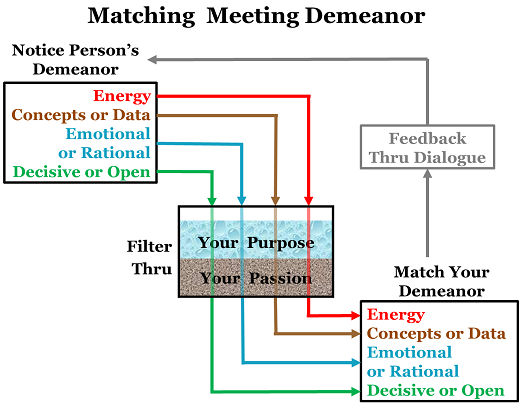
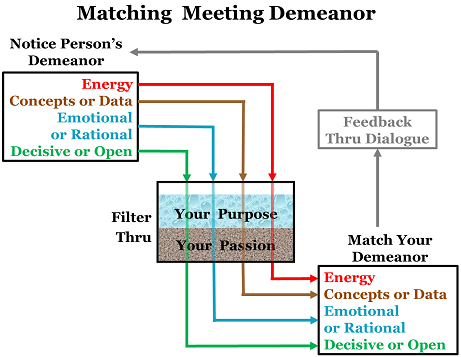
Leadership Tools: Matching Meeting Demeanor
Effective leaders are versatile in their meeting demeanor. They are high energy or calm. They use concepts or data, feelings or logic, decisiveness or patience, as the situation demands.
Leadership Tools: Purpose & Passion, Feedback & Subtlety
To maximize meeting impact, filter your actions through your purpose and passion. Get instant feedback. And match demeanor, don’t just mimic behavior.
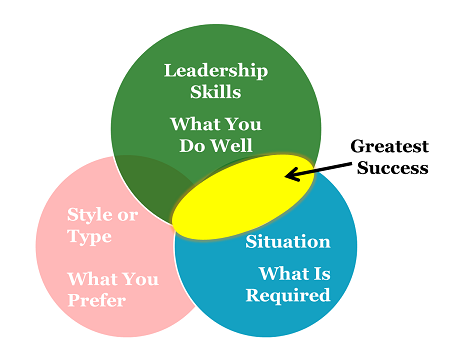
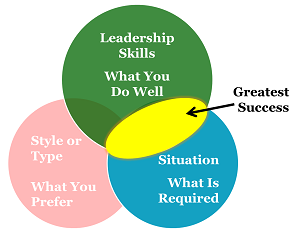
Styles & Types? Or Situations & Tools?
Leaders cannot rest on a certain style or type. Fill your toolbox with leadership skills and be flexible in when you use which tool.
Bottom line: Fill your toolbox with a wide range of leadership skills and be flexible in when you use which tool. You will increase the sweet spot of your leadership and reach your greatest success as a leader.
Styles & Types? Or Situations & Tools?
Allen Slade
In my experience, the leader’s toolbox is a powerful way to think about your leadership. But some people push back, especially fans of leadership styles or personality types.
Styles and Types
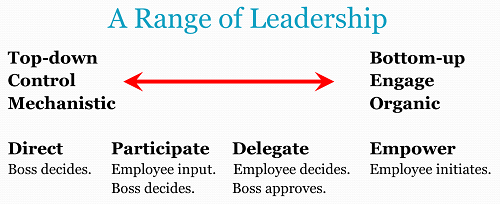
Some leadership advice focuses on changing leaders to be the right style. Be more participative or be more communicative. Be a Theory Y leader. Be a 9,9 leader. Unless you luck into the right situation where this style is always best, one-best-style leadership advice should be avoided.
A somewhat better form of leadership advice is to “find your leadership style” so you understand how you work best. A strategic leader might want to complete and complement her leadership style by hiring a detail oriented manager. Closely related is “find your type” advice using a personality test or the Myers Briggs Type Indicator. If you know your personality type, then you can find situations that fit your personality. Introverts can work on solo analytical projects, while extraverts should find jobs with lots of personal contact.
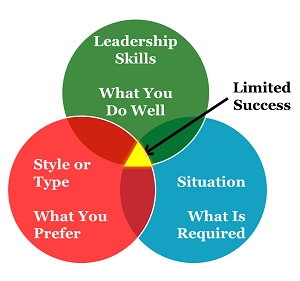 Taken to the extreme, “find your style” or “find your type” leadership limits your success as a leader. Your sweet spot as a leader will be the narrow intersection of skill, style and situation. If your style limits your range of leadership, your success will also be limited.
Taken to the extreme, “find your style” or “find your type” leadership limits your success as a leader. Your sweet spot as a leader will be the narrow intersection of skill, style and situation. If your style limits your range of leadership, your success will also be limited.
Restricting yourself to one preferred leadership style or personality type is like restricting your driving to only certain roads. If you can drive on more roads, you will go further.
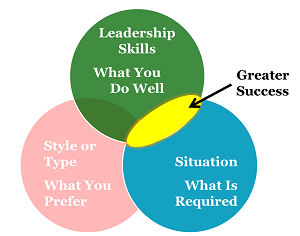 If you take your prefered leadership style or personality type out of the picture, you expand your sweet spot. You can lead in more ways and you will have greater success as a leader.
If you take your prefered leadership style or personality type out of the picture, you expand your sweet spot. You can lead in more ways and you will have greater success as a leader.
For example, my personality is strongly introverted. Yet, to be successful as a consultant, an HR executive and a professor, I stopped acting like an introvert. I developed my public speaking skills. I focused on networking even when I wanted to curl up with a good book. I don’t use my personality as an excuse. If my leadership does not serve me well in a given situation, I try another harder or switch leadership tools.
Situations and Tools
The leader’s toolbox approach expands your choices as a leader:
1. Fill your toolbox with a variety of leadership tools for relationships (communication skills, meeting demeanor, decision making techniques, confidence and emotional intelligence) and tasks (budgeting, scheduling, goal setting, execution and quantitative skills).
2. Pick out the right tool for the situation.
3. Get feedback and adjust as necessary.
Bottom line: To be fully effective as a leader, you must be flexible in your own behavior. A lack of adaptability fundamentally limits you as a leader. You cannot rest on a certain leadership style or preferred type of interaction. You should fill your toolbox with a wide range of leadership skills and be flexible in when you use which tool. You will increase the sweet spot of your leadership and reach your greatest success as a leader.
Leadership Tools: Purpose and Passion, Feedback and Subtlety
Allen Slade
The most effective leaders adapt to the situation, but they are driven by their own purpose and passion. You can stumble by being inflexible. You can stumble if circumstances drive you. The best leader will balance openness to feedback with constancy of purpose.
How do you balance adaptability with purpose and passion? One example is the leadership tool of matching meeting demeanor.
As you match the four aspects of meeting demeanor (energy, concepts or data, emotional or rational persuasion, decisive or open-ended), you need purpose and passion, feedback and subtlety.
Purpose and Passion
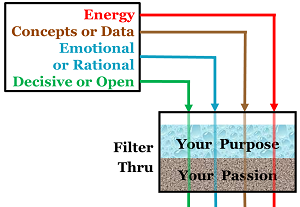 As a leader, your purpose sets your direction. Your passion energizes your actions. Your purpose and passion should filter everything you do, including your meeting demeanor.
As a leader, your purpose sets your direction. Your passion energizes your actions. Your purpose and passion should filter everything you do, including your meeting demeanor.
In a meeting at Microsoft, a vice president, my boss and I were synced up on meeting demeanor. We had medium energy and we were looking at concepts, rationally and decisively. Then, we discussed “what would happen if” we were asked to violate employee confidentiality. Because of my passion for confidentiality, I immediately switched demeanor. I went high energy and made an emotional argument. In other words, I threatened to quit. The meeting quickly broke up, my boss high-tailed it down the hall and I was left standing outside the VP’s office.
The VP apologized the next morning, and I was never asked to compromise my standards. But, even if I had lost my job over this outburst, my passion for confidentiality is so strong that I would have been content with my actions.
Feedback
Leaders have to balance constancy of purpose with openness to feedback. To be effective, you need feedback on your impact.
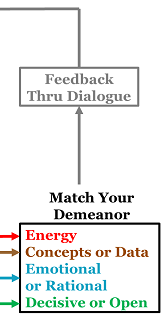 If you have no awareness of others’ meeting demeanor, you will usually not be very effective. If you take a quick snapshot of energy, data vs. concepts etc., at the beginning of the meeting, you will be more effective.
If you have no awareness of others’ meeting demeanor, you will usually not be very effective. If you take a quick snapshot of energy, data vs. concepts etc., at the beginning of the meeting, you will be more effective.
But, just like video is richer than still photos, you want to have continuous feedback on your meeting impact. Watch their body language, voice tone, and what they say to see if you are truly matching up your demeanor.
Match, Don’t Mimic
The wise leader will adjust meeting demeanor directionally to fit the demeanor of others, but not to excess. I suggest matching at a level of 80% to 120%.
- If the other person has much higher energy than you, adjust your energy to 80% of theirs. If they are much lower energy, adjust your energy to 120% of their energy.
- If they are all about concepts, don’t skip the data slides in your presentation. Just touch them lightly and move on.
- If they are absolutely decisive, match their drive to decide, but reserve the right to request a future meeting to follow up on the issue. If you request followup decisively, they are likely to say yes.
Bottom line: Your impact is magnified by matching the meeting demeanor of others in the room. Filter your actions through your purpose and passion. Get instant feedback by observing how your demeanor is impacting the others. And be subtle – match demeanor, don’t just mimic behavior. Then, your meeting influence will grow as the people around you respect your adaptable leadership.